Energy Loss
2024-05-13
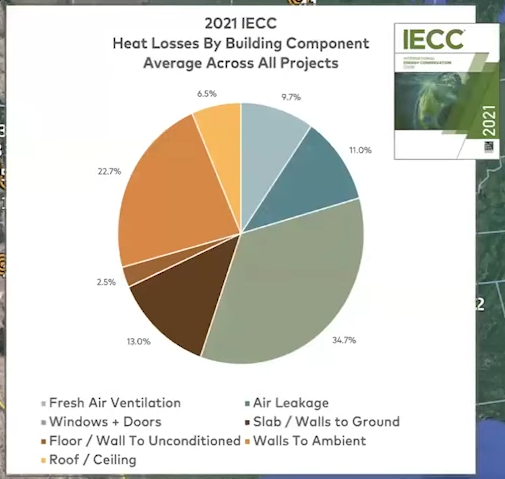
Where is energy lost in buildings?
When using the IECC 2021 Energy Code it looks like this:
| Aspect | Heat loss % |
|---|---|
| Windows + Exterior Doors | 34.7% |
| Exterior Walls | 22.7% |
| Slab / Walls to Ground | 13% |
| Air Leakage | 11% |
| Fresh Air Ventilation | 9.7% |
| Roof | 6.5% |
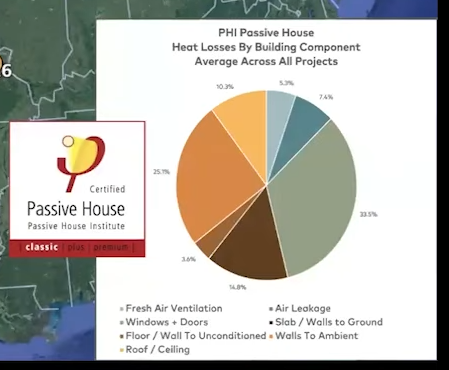
Quite Similar for passive house build:
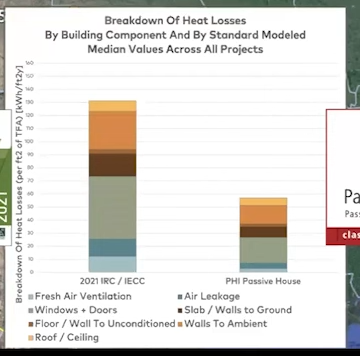
But the overall energy loss is a lot lower.
The Energy loss for windows is as follows:
- Conduction at Window Frame
- Conduction at Glass
- Thermal Bridge @ Window to Wall Connection
- Thermal Bridge @ Glass Edge
- Air Leaks @ Sash/Frame
- Air Leaks @ Window-to-Wall Connection
Recommendations for good windows:
- Fixed
- In-swing, tilt/turn
- Out-swing
- Hopper
- Lift+Slide
Avoid: Sliders, Pivot, Multi-fold accordion, Pass-through
R values for different frame materials:
| Material | R-Value |
|---|---|
| Aluminium | 1.8 |
| Vinyl | 3.3 |
| Wood | 3.2 |
| phC | 3.9 |
| phB | 6.0 |
| phA | 8.1 |
pHC/B/A are passive house graded frames. The glass is not included
When looking at glass it's many questions that need to be answered.
For example a thick 2 pan glass window can deliver the same performance as a think 3 pane glass setup.
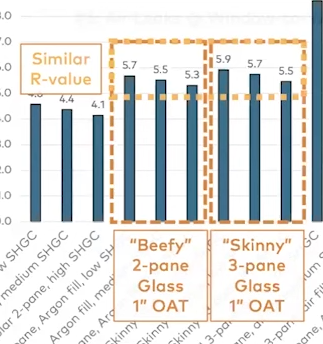
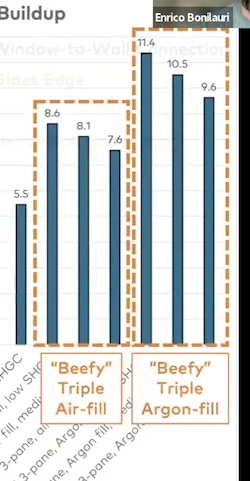
Avoid triple pane glass that has an Overall Thickness less than 1.5"!! Otherwise you pay the premium but don't get the performance benefit
Air vs Argon makes a big difference, however there is a 1% loss of argon for each year.
Energy gain difference with different coatings:
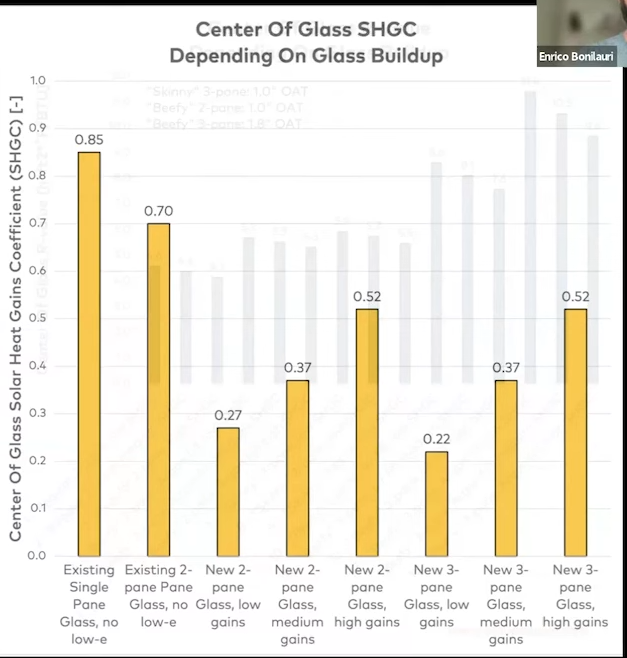
High gains also typically means more daylight entering through the windows.
Summary
- Triple pane glass, ensure it's ticker than 1.5"
- In-swing for egress windows, Lift+Slide for patio doors
- Look into getting a passive house certified frame, can be cost effective
- Argon filling